- ZC MCAL Product Customization And Development Service Manual
- ZC VECTOR FBL Product Engineering Service Manual
- ZC'S Service Based On NXP S32K3 Series Functional Safety Package
- ZC LIN Consistency Testing Service
- ZC Provides Basic Software Solutions Based on Infineon MOTIX™ Chips
- ZC'S Services Based on NXP S32K3 Series Functional Safety Package
- ZC E2E Testing Service Manual
- MIGRATION GUIDE FROM TRICORE PLATFORM TO ARM CORTEX-R52/R52+
- ZC RTE Testing Service Manual
- ZC.MUNIU NXP S32K1 CYBERSECURITY SECURITY SERVICE MANUAL
- ZC Embedded Automation Testing Service Manual
- MIGRATION GUIDE: FROM RENESAS RH850 G3MH/G3KH TO ARM CORTEX-R52/R52+
- ZC ASPICE SWE04 UNIT TESTING INTRODUCTION
- ZC MCAL DEVELOPMENT PROCESS INTRODUCTION
- ZC Functional Safety Engineering Service Manual
- ZC Safety Library Service Manual
- ZC VECTOR MICROSAR Product Engineering Service Manual
- ZC MCAL Product Customization And Development Service Manual
- ZC ECU Controller Development Functional Service Manual
- ZC Software Testing Engineering Service Manual
- ZC HIL Testing Engineering Service
- ZC Test Factoy Engineering Service Manual
- ZC ADAS Domain Controller Based on Infineon MCU TC397
- ZC Gateway Product Manual
- Portable Charger Product Manual
- AC Charging Pile Product
The MCAL information security library provided by NXP contains the Csec kernel driver Crypto_Cse and its supporting Crypto modules.
Based on the MCAL cybersecurity library provided by NXP, ZhiCong adds the Csm module, CryIf module and KeyM module of CryptoStack to adapt to the Crypto module of the NXP kernel driver, and integrates SecOC, SecureLog.
Ø Csm: Located at the service layer, it is used to handle user information security task configuration management and scheduling.
Ø CryIf: located in the ECU abstraction layer, it is used to implement secure communication between the Csm module and the Crypto module.
Ø KeyM module: key management, which is used to realize the interaction between keys and the underlying Csec store.
Ø SecOC: In-vehicle Secure Communications, used to protect network communications between ECUs in a vehicle, is currently an effective information security program on in-vehicle networks.
Ø SecureLog: Stores vehicle abnormal status information to effectively protect the controller's information security on the client side.
ZC uses NXP MCAL information security libraries for configuration according to customer needs, and can also provide appropriate integration testing services to meet customer information security engineering needs.

Based on the information security libraries provided by NXP and in combination with the KnowledgeFrom Information Security Protocol Stack, it can be applied to automotive controllers with information security requirements. For example:
l Remote Controller (TBOX)
l In-Vehicle Infotainment (IVI)
l Body Controller (BCM)
l Electric Power Steering Controller (EPS)
l Wiper Controller
By integrating the information security module into the automotive electronic controller product, in addition to meeting the requirements of the basic elements of security such as confidentiality, integrity, availability, etc., it also has the ability to meet the needs of the basic software can be cut, configurable, real-time and other characteristics.
3 ZC.MuNiu Technical services
3.1 CryptoStack Encryption Protocol Stack

ZC.MuNiu encryption protocol stack is mainly composed of four modules: Csm, CryIf, Crypto, and KeyM. The Csm module implements the encryption algorithm requirements for Cybersecurity software or hardware needed by users, such as AES-128, CMAC,, TRNG, etc., through the configuration of CsmJobs, and provides interfaces for user calls. The CryIf module functions to connect the service layer Csm module with the hardware abstraction layer Crypto module, protecting the integrity and confidentiality of data through security functions such as encryption, decryption, verification, and authentication. The Crypto module provided by NXP implements the transfer of information data between the main core and the Csec encryption core. The KeyM module implements the management of keys, including the parsing and verification of keys and certificates downloaded into the ECU, and connecting to the CSEC kernel driver to store keys into the CSEC protected area.
3.2 SecOC
SecOC, FvM, PduR and other modules are configured to meet SecOC requirements; Csm, CryIf, Crypto (HW) and other modules are configured to realize the encryption function of SecOC authentication.SecOC protects the data by using MAC checksum and Freshness Value (FV), and checksum generates the MAC value by using the CMAC algorithm of AES-128. When sending, the Secured I-PDU is composed by intercepting some values of MAC and FV, and sent to the target ECU; the target ECU checks the MAC value and FV value after receiving the Secured I-PDU, and if the check passes, it indicates that the message data is valid.
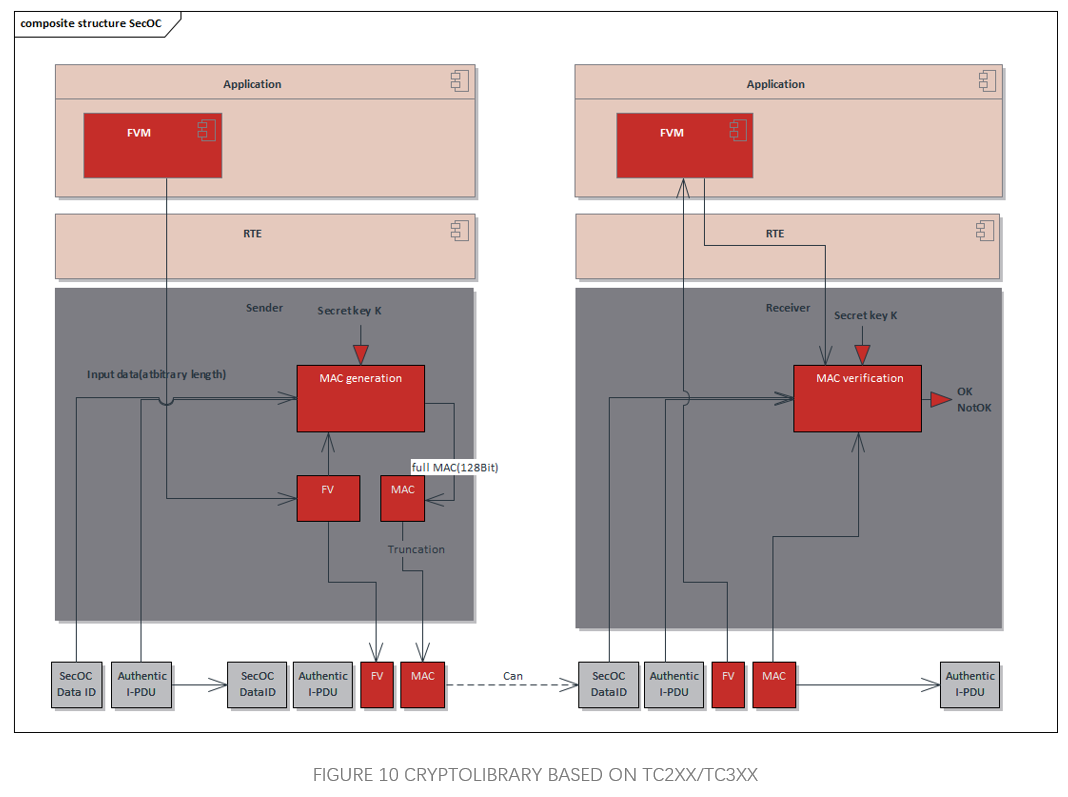
3.3 Secure Log
Security logs can be used to record information such as abnormal problems or records of authorized users generated in the process of secure communication, which can facilitate the troubleshooting of controller development as well as risk control. When the ECU generates information security vulnerabilities, the log information can be used to quickly analyze the reasons for the impact and the impact of the function, to improve the robustness of code development, and to reduce a series of impacts caused by information security vulnerabilities.
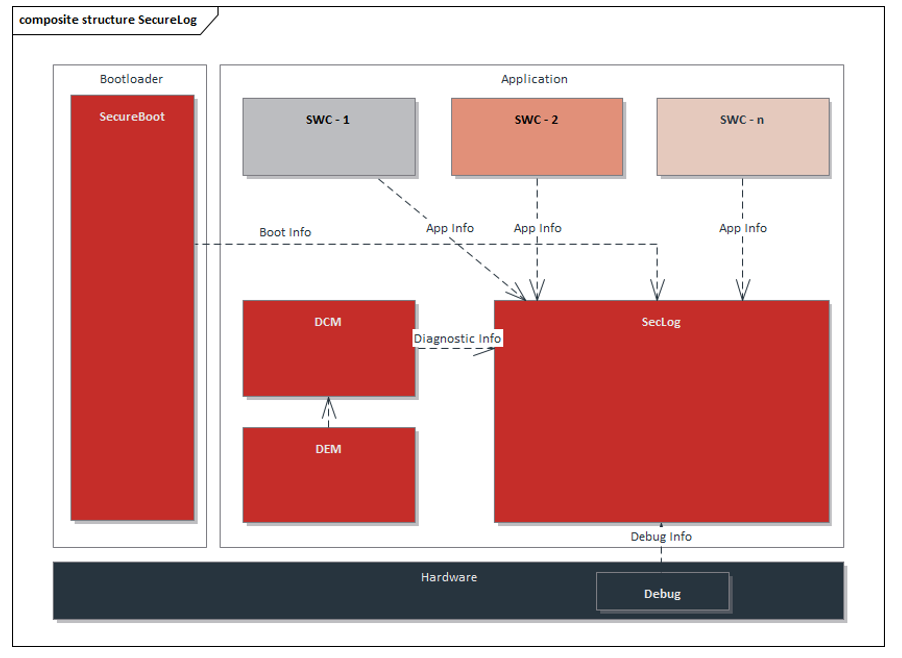
3.4 Secure Debug
Most controllers nowadays are equipped with hardware-based debugging functions for on-chip debugging processes. Secure JTAG mode refers to the use of a Challenge/Response-based authentication mechanism to restrict JTAG access. Any access to the JTAG port is checked, and only authorized debugging devices (those with the correct response) can access the JTAG port; unauthorized JTAG access attempts will be denied. During production or the offline phase, it is necessary to disable or lock the related debugging diagnostic interfaces. Disabling means that no connection can be established with the hardware debugging interface, while locking means that the hardware debugging interface is protected and can only be accessed through secure debugging unlock.
ZC has developed different secure debugging feature plans for chips from various manufacturers. For example, for NXP S32K1xx series chips, the Debug function can be enabled and disabled through secure diagnostic methods, with Secure Diagnostic ensuring that authorized users can perform debugging functions.
3.5 Configuration Service
In order to meet the different project requirements of customers and improve the scalability of CryptoLibrary, the Configuration Tool from MuNiu realises the configurability of CSM, CryIf, Crypto, KeyM and other modules as well as cryptographic kernel. Customers can complete the configuration of CSM, CryIf, Crypto, KeyM and other modules on the configuration tool according to different needs, can generate configuration code files, and the generated configuration file can be integrated into the project; and can be configured according to the needs of the corresponding Csec module driver function to achieve the interface call.
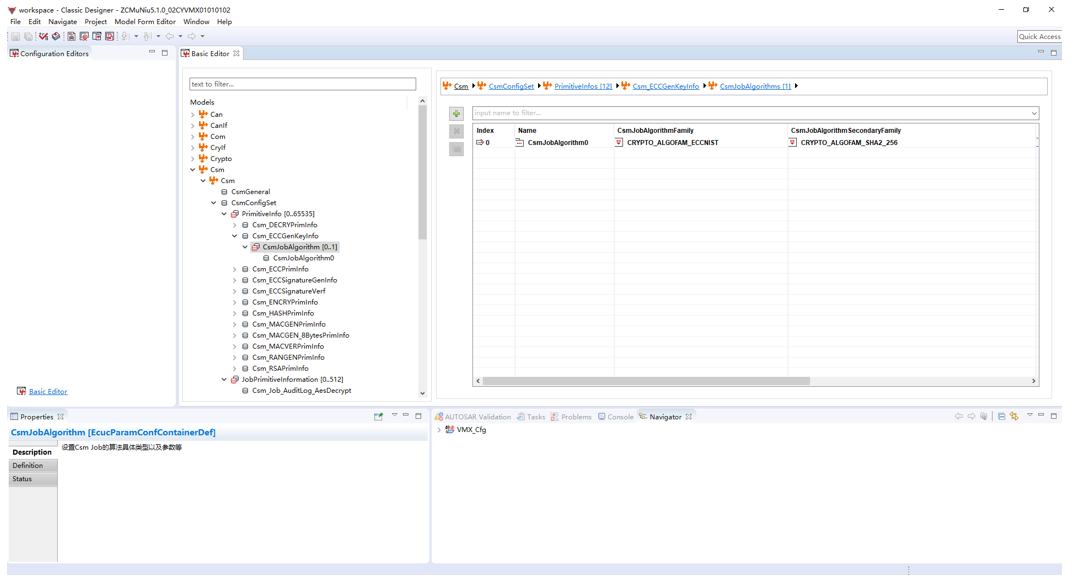
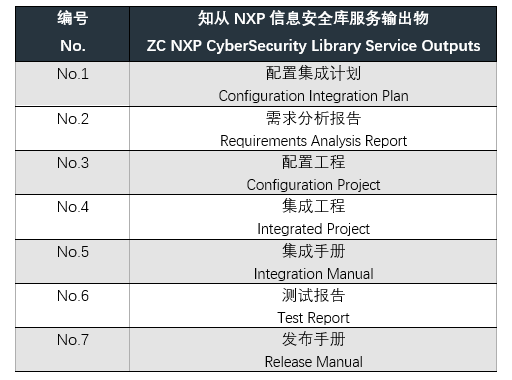
4 Project implementation
Click to download the product manual